Computational Scaling Relationships Predict Experimental Activity and Rate Limiting Behavior in Homogenous Water Oxidation
Abstract
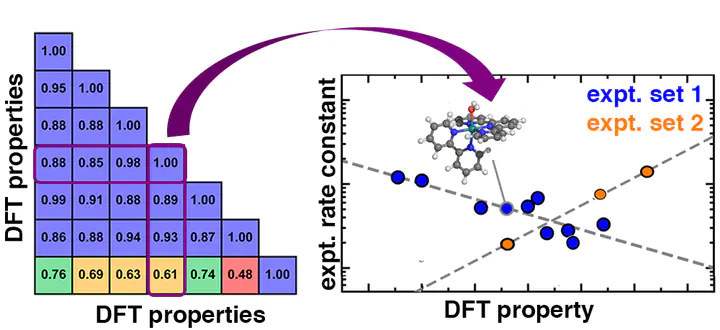
While computational screening with first-principles density functional theory (DFT) is essential for evaluating candidate catalysts, limitations in accuracy typically prevent the prediction of experimentally relevant activities. Exemplary of these challenges are homogeneous water oxidation catalysts (WOCs) where differences in experimental conditions or small changes in ligand structure can alter rate constants by over an order of magnitude. Here, we compute mechanistically relevant electronic and energetic properties for 19 mononuclear Ru transition-metal complexes (TMCs) from three experimental water oxidation catalysis studies. We discover that 15 of these TMCs have experimental activities that correlate with a single property, the ionization potential of the Ru(II)–O2 catalytic intermediate. This scaling parameter allows the quantitative understanding of activity trends and provides insight into the rate-limiting behavior. We use this approach to rationalize differences in activity with different experimental conditions, and we qualitatively analyze the source of distinct behavior for different electronic states in the other four catalysts. Comparison to closely related single-atom catalysts and modified WOCs enables rationalization of the source of rate enhancement in these WOCs.