The Protein’s Role in Substrate Positioning and Reactivity for Biosynthetic Enzyme Complexes: The Case of SyrB2/SyrB1
Abstract
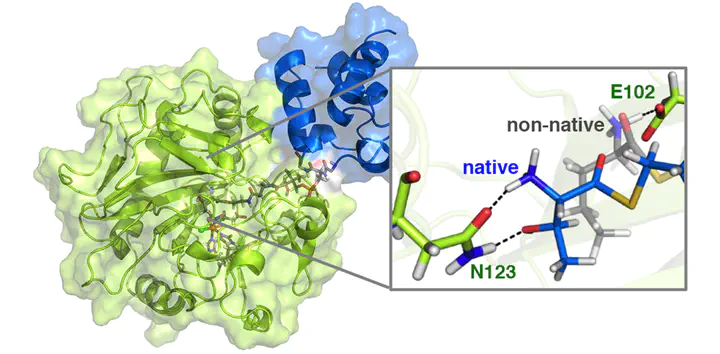
Biosynthetic enzyme complexes selectively catalyze challenging chemical transformations, including alkane functionalization (e.g., halogenation of threonine, Thr, by the non-heme iron halogenase SyrB2). However, the role of complex formation in enabling reactivity and guiding selectivity is poorly understood, owing to the challenges associated with obtaining detailed structural information on the dynamically associating protein complexes. Combining over 10 μs of classical molecular dynamics of SyrB2 and the acyl carrier protein SyrB1 with large-scale QM/MM simulation, we investigate the substrate–protein and protein–protein dynamics that give rise to experimentally observed substrate positioning and reactivity trends. We confirm the presence of a hypothesized substrate-delivery channel in SyrB2 through free energy simulations that show channel opening with a low free energy barrier. We identify stabilizing interactions at the SyrB2/SyrB1 interface that are compatible with phosphopantetheine (PPant) delivery of substrate to SyrB2. By sampling metal–substrate distances observed in experimental spectroscopy of native SyrB2/SyrB1-PPant-S-Thr and non-native substrates, we characterize essential protein–substrate interactions that are responsible for substrate positioning, and thus, reactivity. We observe the hydroxyl side chain and terminal amine of the native Thr substrate to form cooperative hydrogen bonds with a single N123 residue in SyrB2. In comparison, non-native substrates that lack the hydroxyl interact more flexibly with the protein and therefore can orient closer to the Fe center, explaining their preferential hydroxylation.