Stable Surfaces That Bind Too Tightly: Can Range-Separated Hybrids or DFT+U Improve Paradoxical Descriptions of Surface Chemistry?
Abstract
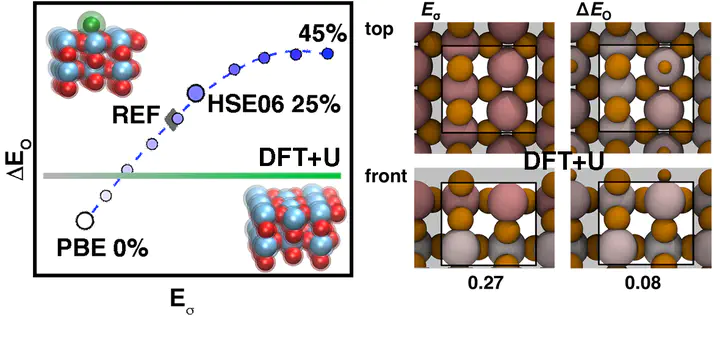
Approximate, semilocal density functional theory (DFT) suffers from delocalization error that can lead to a paradoxical model of catalytic surfaces that both overbind adsorbates yet are also too stable. We investigate the effect of two widely applied approaches for delocalization error correction, (i) affordable DFT+U (i.e., semilocal DFT augmented with a Hubbard U) and (ii) hybrid functionals with an admixture of Hartree–Fock (HF) exchange, on surface and adsorbate energies across a range of rutile transition metal oxides widely studied for their promise as water-splitting catalysts. We observe strongly row- and period-dependent trends with DFT+U, which increases surface formation energies only in early transition metals (e.g., Ti and V) and decreases adsorbate energies only in later transition metals (e.g., Ir and Pt). Both global and local hybrids destabilize surfaces and reduce adsorbate binding across the periodic table, in agreement with higher-level reference calculations. Density analysis reveals why hybrid functionals correct both quantities, whereas DFT+U does not. We recommend local, range-separated hybrids for the accurate modeling of catalysis in transition metal oxides at only a modest increase in computational cost over semilocal DFT.